Underwater ROVs in 2025: Everything You Must Know About Remotely Operated Vehicles
What is an underwater ROV? Learn how remotely operated vehicles work, their applications, key features, and the latest tech in marine robotics.
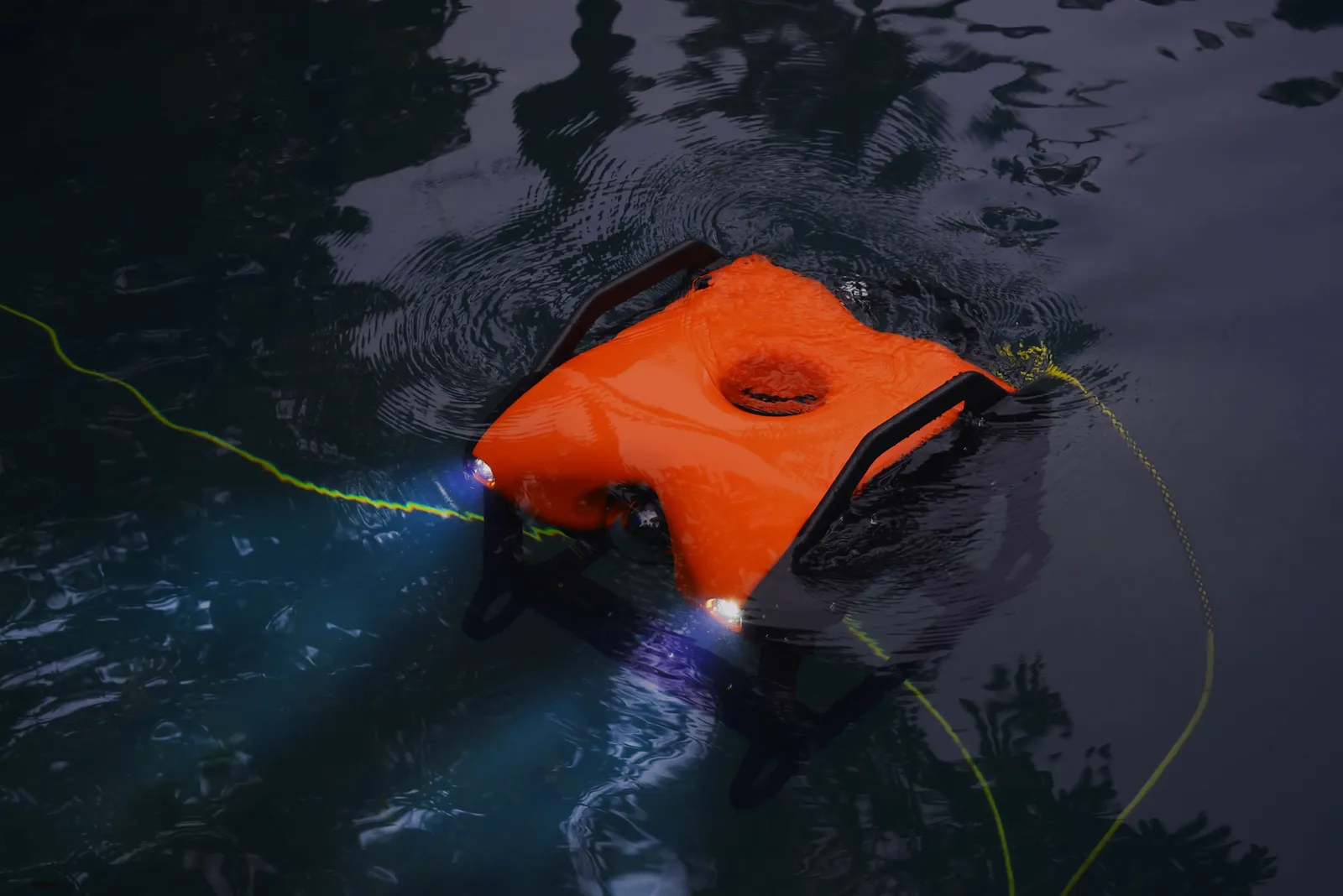
A Remotely Operated Vehicle (ROV) is an unmanned underwater robot that’s piloted from the surface using a tether. These machines are built to explore, inspect, and work in places that are too deep, dangerous, or impractical for divers.
ROVs are widely used in industries like oil & gas, marine research, defense, and underwater infrastructure maintenance - basically, anywhere that requires eyes and tools beneath the water.

How Do ROVs Work?
An ROV is typically connected to a control unit on the surface (usually on a ship, dock, or platform) via an umbilical tether. This tether supplies power and transmits data like video feeds, sonar readings, and sensor outputs. Operators use joysticks or control software to maneuver the ROV in real time.
Core Components of an ROV
- Buoyant Frame: Lightweight but strong, often with syntactic foam for deep dives
- Thrusters: Enable movement in multiple directions with precision control
- Cameras & Lighting: High-definition or 4K video with LED lights for dark waters
- Manipulator Arms: For interacting with the environment or retrieving objects
- Tether Cable: Handles power and data transmission
- Sensor Suite: Includes sonar, depth sensors, GPS (surface only), and optional payloads
Key Applications of Underwater ROVs
ROVs are used across a wide spectrum of fields:
- Oil & Gas: Inspect pipelines, risers, anchors, and offshore rigs
- Maritime & Ports: Ship hull checks, dock infrastructure inspection
- Dams & Tunnels: Identify sediment build-up, corrosion, or structural damage
- Defense: Surveillance, search and recovery, mine detection
- Aquaculture: Monitor fish health, net integrity, and seabed conditions
- Research: Ocean mapping, habitat monitoring, archaeological exploration
- Search & Rescue: Locate missing persons or sunken equipment in low-visibility zones
What Makes a Good ROV?
A few features can set apart a high-performance ROV from an average one:
- Depth Rating: Determines how deep it can go. Industrial ROVs go hundreds of meters down
- Stability: Important for data accuracy, especially in turbulent water
- Payload Versatility: Ability to attach different tools or sensors
- Live Feedback: Real-time visuals and sensor data make all the difference
- Ease of Use: Good UI/UX for pilots, portable design, and smart diagnostics
The Latest in 2025: Smarter, Smaller, Tougher
With AI, machine learning, and sensor miniaturization, ROVs in 2025 are more capable than ever. They’re easier to deploy, smarter in navigating underwater terrain, and better at collecting actionable data.
Many of today’s ROVs are designed to operate in tight environments with just one operator, and offer swappable payloads that make them mission-ready in minutes.
EyeROV’s Role in Modern Marine Operations
EyeROV is a worldwide underwater robotics company developing versatile and reliable ROVs tailored for real-world operations. Some of our flagship systems include:
- TUNA: High-Performance observation-class ROV built for Deep-Sea operations, featuring advanced payload support and Autonomous Navigation.
- TROUT: Military-Grade ROV engineered for Deep-Sea missions, featuring Autonomous-Navigation, Advanced Imaging, and Rugged Construction.
- iBoat Alpha: Autonomous Surface Vessel (ASV) designed for Remote Inspections, Surveillance, and Monitoring with advanced sensor integrations.

Our systems support multiple industries, with tools like ultrasonic thickness gauges, imaging SONAR, manipulators, and an AI-powered analytics suite called EVAP.
Interested in ROVs?
Explore EyeROV TUNA or reach out to learn how we can help with your underwater inspection, survey, or research needs.